FORM 2-PHYSICS-TOPIC 6-MOTION IN STRAIGHT LINE
Motion is the change of position of an object from one place to another. There are two types of motions; i.Circular motion-Is the motion of an object in a circle. Examples; a/. motion of the electron around the nucleus of an atom b/.revolutionary movement of the earth around the sun. ii.Linear motion-Is the motion of an object in a straight line.
Distance and Displacement
Speed and Velocity
Acceleration
Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity or is the change in velocity per unit time Mathematically. Acceleration, a = (final velocity, v – initial velocity, u)/time, t
Velocity Time-graph
Interpret velocity time-graph
This is velocity against time graph. Consider a body accelerating uniformly from rest to a certain velocity v within time t. This can be represented graphically as shown below;
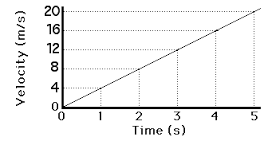
Distance
- The distance x moved by the body is given by the area under the curve.
- In this case is the area of triangle OBC.
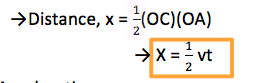
Acceleration.
- The acceleration is given by the slope of the triangle OBC.
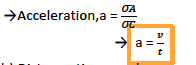
The Acceleration of a Body
Determine the acceleration of a body
Example 1
A car starts from rest and accelerates to a velocity of 120m/s in one minute. It then moves with this speed for 40seconds finally decelerates to rest after another 2 minutes. Calculate;
- the distance travelled
- the total time taken for the whole motion
- the deceleration
- the average velocity
Soln
1st stage; acceleration u =0, v = 120m/s,t1 =1min=60s
2nd stage; uniform vel u=v=120m/s,t2=40s
3rd stage; Deceleration u=120m/s,v=0,t3=2min=120s
- 1st stage; s =average vel x time = ( (120+0)/2)60 = 3600m
- 2nd stage; s = vt = 120 x 40 = 4800m
- 3rd stage; s = average vel x time = ((v=u)/2)t = ((120+0)/2)120 = 7200m
Total distance, s T =3600+4800+7200 =15600m
Total time taken = 60 + 40 + 120 = 220s
from v = u + at
120 = 0 + 60a
60a = 120
a = 2m/s.
Average velocity = total distance/time
va = 15600/220
va = 71m/s
The Concept of Retardation
Explain the concept of retardation
Deceleration (retardation) is the rate of decrease of velocity or is the decrease in velocity per unit time. Uniform acceleration or retardation Is the one whereby the rate of increase or decrease of velocity is constant or it doesn’t change.
Note;
- when a body starts from rest or is brought to rest, its velocity is zero
- when the velocity of a body is constant or uniform, its acceleration is zero
- when the velocity of a moving object increases, its acceleration becomes positive
- when the velocity of a moving object decreases, its acceleration becomes negative called retardation.






