FORM 2-PHYSICS-TOPIC 6-MOTION IN STRAIGHT LINE
Motion is the change of position of an object from one place to another. There are two types of motions; i.Circular motion-Is the motion of an object in a circle. Examples; a/. motion of the electron around the nucleus of an atom b/.revolutionary movement of the earth around the sun. ii.Linear motion-Is the motion of an object in a straight line.
Distance and Displacement
Speed and Velocity
Acceleration
Equations of Uniformly Accelerated Motion
Equation of Uniformly Accelerated Motion
Derive equation of uniformly accelerated motion
There are three equations of motion;
Newton’s first equation of motion
It is given by; v = u + at
whereby;
- u = initial velocity
- v = final velocity
- a = acceleration
- t = time taken
PROOF;
From the formula of acceleration; a = (v-u)/t
- at = v – u at + u = v
- v = u + at proved!
Newton’s second equation of motion
It is given by
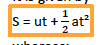
whereas;
- s=distance travelled
- u=initial velocity
- t=time taken
- a=acceleration
PROOF;
Suppose an object starts from rest with intial vel,u to final vel,v after time t The distance ,S moved is given by S = Average vel x time S =( (u+v)/2)t
Substitute Newtons first eqn,gives; S = ((u+u+at)/2)t
S = ((2u+at)/2)t
S = ut + 1/2at. proved!
Newtons third equation of motion
It is given by V2 = U2+ 2as
where v=final velocity; u =initial velocity; a = acceleration; s = distance covered.
PROOF
From Newton’s first eqn; v = u + at
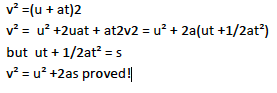
Equations of Accelerated Motion in Daily Life






