Work
Energy
Power
The Concept of Power
Explain the concept of power
Power is the rate of which work is done.
- It is a measure of the rate at which energy changes.
- This means that whenever work is done energy changes into a different form.
The S.I Unit of Power
State the S.I unit of power
The SI unit of power is Jules per second J/S or watts, W.
1 Joules per second = 1 watt
When 1 Joules of work is done per second the power produced is a watt. Watt is the unit for measuring electrical power.
The Rate of Doing Work
Determine the rate of doing work
Suppose that two cranes each lift objects having masses of 200kg to a height of 12m. Crane A lifts its object in 10sec while crane B requires 15sec to lift its object. Assume they lift the objects at a constant velocity they do the same amount of work.
Work done = GPE
= Mgh
= (200kg) (9.8m/s2)(12m)
= 23520J
Each did a work that was equivalent to 23520J.
What is different for the two cranes is the rate at which they did the work or their generation of power.
The power of crane A can be calculated by;
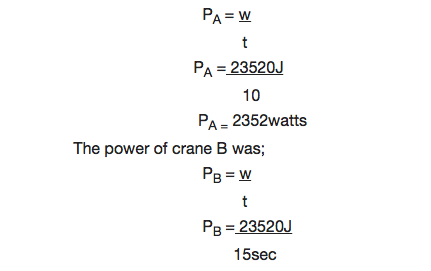
PB = 1568 watts.
Example 5
How much power is required to accelerate a 1000kg car from rest to 26.7m/s in 8sec?
Solution:
The work done on the car increases its Kinetic energy.
Work done = AKE
½ MV2 – ½ MV2
The power required is given by:
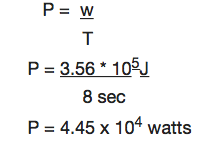
Example 6
Car engine is rated in horsepower (hp) where 1hp = 746watts. What is the required power measured in horsepower?
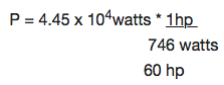
Since work causes a change in energy. DE power can be considered as the rate of change of energy.
P = DE/t






