Concepts of Measurement
Basic Fundamental Quantities
A Fundamental Quantity
Define a fundamental quantity
Physical quantity:Is any character which can be measured by an instrument.
A Unitis the standard which is used to explain measurement of a body.Eg; kilogram, metre, second etc.
Fundamental quantitiesare numbers that we need to describe the world around us, which we cannot express in terms of "simpler," more basicquantities. Here is an example: My weight is not afundamental quantity, because it depends on how much stuff makes up my body.
Three Basic Fundamental Quantities of Measurement
Mention three basic fundamental quantities of measurement
Basic fundamental quantitiesare physical quantities from which other physical quantities are derived from. This includes three quantities namely mass, length and time.
The S.I Unit of Fundamental Quantity
State the S.I unit of fundamental quantities
SI unit (International system of units): Is the system of units which is used internationally to measure three basic physical quantities.
SI units of fundamental quantities
| Basic physical quantity | SI unit |
| Mass | Kilogram (kg) |
| Length | Meter (m) |
| Time | Second(s |
Metric system
Is an international system which is a decimal based system, consequently, conversions from one unit to another within the metric system can accomplished by multiplying or dividing by ten or power of ten.
Note: With the exception of temperature, amount of substance and luminous intensity international other units of measurement that are smaller or larger than the most commonly used units are expressed by attaching a prefix to the most commonly used units.
More than 1 unit
- Giga(G) = 1,000,000,000 (10ˆ9)
- Mega(M) = 1,000,000 (10ˆ6)
- Kilo(K) = 1,000(10ˆ3)
- Hector (h) = 100(10ˆ2)
- Decca(da) = 10(10ˆ1)1
Less than 1 unit
- Deci (d) = 1/10 (10ˆ-1)
- Cent (c) = 1/100(10ˆ-2)
- Mill (m) = 1/1000 (10ˆ-3)
- Micro(μ) = 1/1,000,000(10ˆ-6)
Appropriate Instruments for Measuring Fundamental Quantities
Use appropriate instruments for measuring fundamental quantities
Length, l
Length is the distance between two points, objects or space.The SI unit of length is meter(m). Other commonly used units are kilometer(km) and centimeter(cm).
1km = 1000m
1m = 100cm
The instrument used to measure length is the metre rule.
How to read the metre rule:Owing to the thickness of the wood,the eye must always be placed vertically above the mark being read, in order to avoid errors due to parallax.
Measuring of length (diameter) of small objects.
The diameter of small objects is measured by using two instruments:
- Vernier caliper
- Micrometer screw gauge
A venier caliper is the instrument used to measure length to the accuracy of 0.01cm.It is used to measure lengths to the range of 1.0cm to about 12.0cm.The figure below describe the structure of vernier caliper.
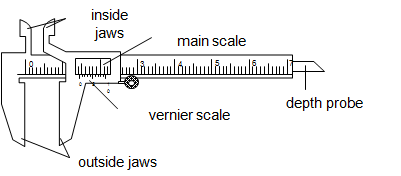
The main scale is graduated in centimeter (cm) while the vernier scale is graduated in millimeter (mm).The vernier scale is a short scale 9mm long divided into 10 equal parts, so that the difference in length between a vernier division and the main scale division is 0.1mm or 0.01cm.
The inside jaws are used to measure the inside diameter while the outside jaws are used to measure outside diameter.The vernier slides over the main scale.
How to read
- The main scale reading is recorded. This is the reading which precedes the zero mark of the vernier scale.
- The vernier scale reading is recorded by reading the mark on it which coincide with a mark on the main scale (i.e. vernier scale reading x 0.01cm).
- The summation of these two readings is the length of the object measured.
A micrometer screw gauge:Is an instrument used to measure length to the accuracy of 0.001cm(0.01mm).It is used to measure the diameters of wires and ball bearings. It can measure small lengths up to about 2.5cm.The diagram below describes the micrometer screw gauge.
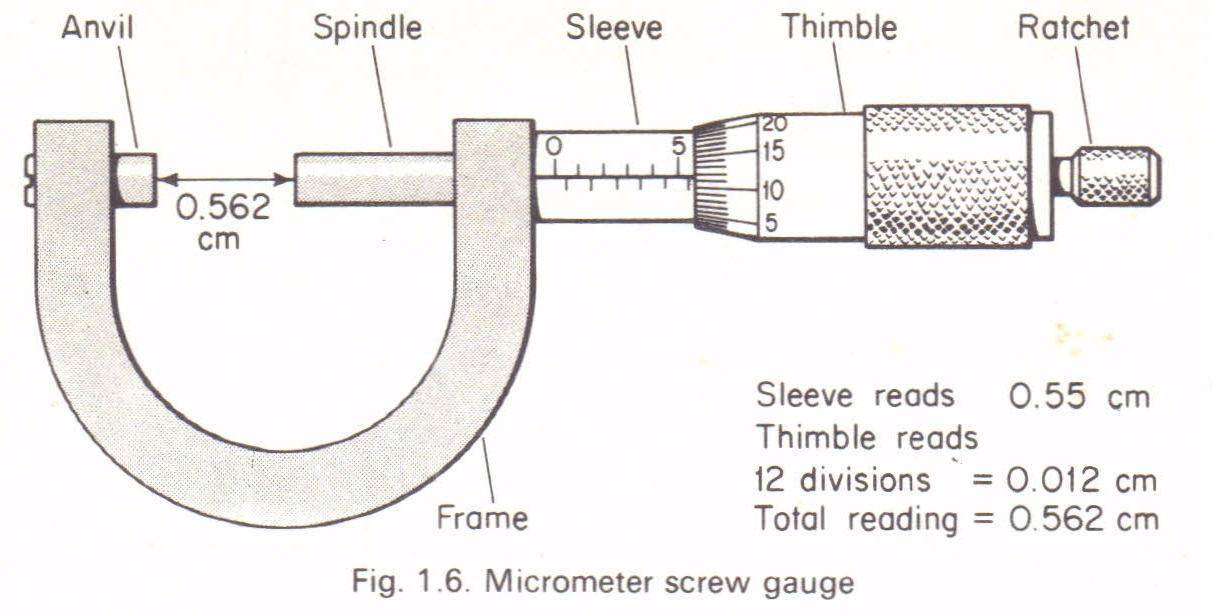
It consists of a spindle which is fitted with a graduated thimble. The screwed portion of a spindle is totally enclosed to protect it from damage.The pitch of the screw is 0.5mm, so that the spindle moves through o.o5cm for each complete turn.
The anvil and the spindle grip the measured object between them. The ratchet prevents the user from using undue pressure. The sleeve is graduated in mm, each graduation represent one complete turn of the screw.
How to read a micrometer screw gauge:
- Sleeve reading is recorded. This gives the units and the first two decimal places in mm.
- Thimble reading is then recorded. This gives the third decimal place (thimble reading x 0.001mm).
- The summation of these two readings gives the diameter of the object under measurement.
Precautions when using a micrometer screw gauge.
- Before use,the faces of anvil and spindle should be wiped clean to remove any dirty particle which would give false readings.
- Check and record for zero error then + or –the correction to the final answer.
Mass
Mass of a body is the amount of matter it contains. The SI unit of mass is kilogram(kg). Other commonly used units are gram(g) and tones(t).
1kg = 1000g
1t = 1000kg
The mass of a body doesn’t change from place to place. The instrument used to measure mass is called abeam balance.
Difference between mass and weight:
| Mass | Weight |
| Is the amount of matter contained | Is the force by which the earth pull a body to its centre |
| SI unit is kilogram | SI unit is Newton |
| Doesn’t vary from place to place on the earth’s surface | Varies from place to place on the earth’s surface |
| Measured by beam balance | Measured by a spring balance |
Time
Is the gap between two occasions or events.The SI unit of time second(s). Other units used are minutes (min), hour(h),day etc.
1min = 60s
1h = 3600s
1day = 86400s
The instruments for measuring time are clocks and watches.







