A force is an interaction that causes a change. In mechanics, a force is an interaction that causes a change in velocity (an interaction that causes acceleration).
Concept of Force
Types of Force
Effects of Force
The Effects of Forces
Identify effects of forces
A force acting on an object may cause the object to change shape, to start moving, to stop moving, to accelerate or decelerate.
When two objects interact with each other they exert a force on each other, the forces are equal in size but opposite in direction.
Resultant force
The forces acting on an object can be replaced with a single force that causes the object to behave in the same way as all the separate forces acting together did, this one overall force is called theresultant force.
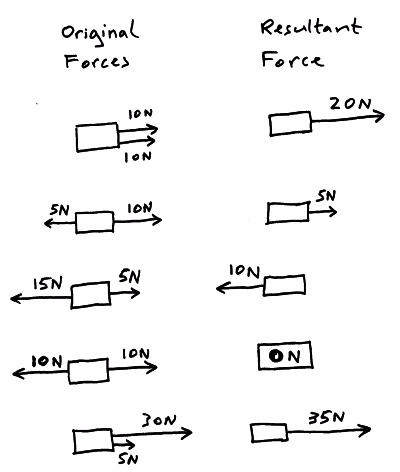
If the resultant force acting on an object is ZERO then:
- The object will remain stationary if it was stationary when the resultant force became zero.
- Move at a constant (steady) speed in a straight line if it was moving when the resultant force became zero.
If the resultant force acting on an object is NOT ZERO then:
- The object will accelerate or decelerate (speed up or slow down).
The Effects of Forces on Materials
Justify the effects of forces on materials
Example 3
A rectangular bar having a cross-sectional area of 80 mm2has a tensile force of 20 kN appliedto it. Determine the stress in the bar.
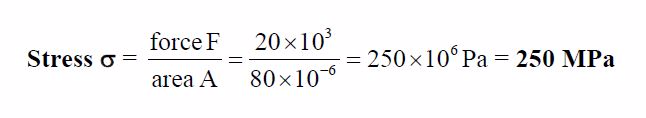
Example 4
A circular section cable has a tensile force of 1 kN applied to it and the force produces a stress of7.8 MPa in the cable. Calculate the diameter of the cable.

Example 5
A split pin requires a force of 400 N to shear it. The maximum shear stress before shear occurs is120 MPa. Determine the minimum diameter of the pin.







