FORM 2-PHYSICS-TOPIC 7-NEWTON'S LAW OF MOTION
NEWTON'S LAW OF MOTION
1st law of Motion
2nd law of Motion
Conservation of linear Momentum
Difference between Elastic and Inelastic Collisions
Distinguish between Elastic and Inelastic Collisions
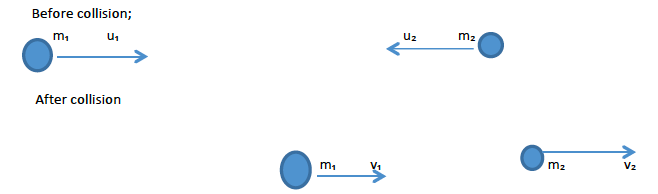
Elastic collision
This is the type of collision whereby each body moves with a separate velocity after collision. In this type of collision both energy and momentum are conserved.
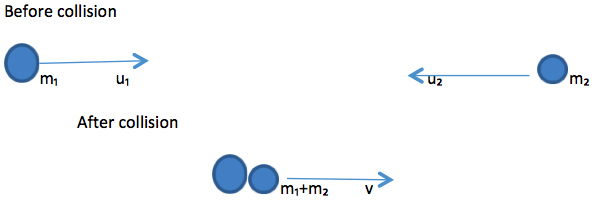
Inelastic collision
Is the type of collision whereby all bodies move with the same velocity after collision. This velocity is known as common velocity. In this type of collision energy is not conserved, only momentum is conserved.
Impulse is the change of momentum which is given asm the product of force and the time taken to change momentum.
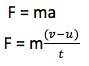
F = mv – mu –Ft is the impulse of a force which is given by mv – mu.
The Principle of Conservation of Linear Momentum
State the principle of conservation of linear Momentum
Principle of conservation of linear momentum states that, “When two or more bodies acts upon one another; that is when they collide their total momentum remains constant, provided that there is no external force acting”
Momentum before collision = Momentum after collision
Consider two bodies of masses m₁ and m₂ moving with initial velocities u₁ and u₂ and then move with final velocities v₁ and v₂ respectively after they collide one another.
From the principle of conservation of momentum: Momentum before collision = Momentum after collision
m₁u₁ + m₂u₂ = m₁v₁ + m₂v₂
The Principle of Conservation of Linear Momentum in Solving Problems
Apply the principle of conservation of linear momentum in solving problems
Activity 2
Apply the principle of conservation of linear momentum in solving problems





