Concept of Magnetism
Magnetisation and Demagnetisation
Magnetic Fields of a Magnet
Earth's Magnetic Field
The Phenomenon of Earth's Magnetism
Explain the phenomenon of earth's magnetism
Earth is imagined as a single big magnet, with its south seeking pole near the geographic north called a north magnetic pole and the north seeking pole is near geographic south pole called south magnetic pole.
The earth behaves as if at its center there is a short piece of a bar magnet inclined at a small angle to its rotation (spinning) axis. When a bar magnet is hanged horizontally with a string, it will oscillates for a short time and then comes to rest with its poles pointing in the N-S direction due to the earth’s magnetic field.
This gives a notion that the earths north pole is in the southern hemisphere where any magnets north pole will always point.The two earth’s magnetic poles are joined by a line called magnetic meridian.The geographic meridian joins the true north and true south.
Direction of Earth's Magnetic Field
Determine direction of earth's magnetic field
Compass needle:Is a thin magnet balanced on a point, usually at the center of gravity used to identify N-S direction.Spinning a compass needle, it will eventually come to rest with its poles pointing to the N-S direction.This gives direction at any point on the earth’s surface
The Earth's Magnetic Lines of Force about a Bar Magnet
Locate the earth' magnetic lines of force about a bar magnet
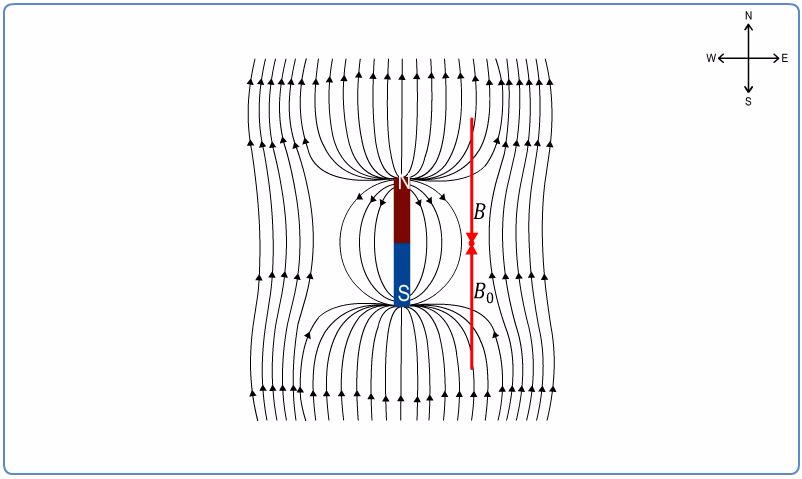
The magnetic field lines around a bar magnet can be mapped with the help of a magnetic compass. The magnetic field lines due to a bar magnet are closed loops. They leave at the north pole and enter at the south pole. When you plot the magnetic field lines around a bar magnet, the horizontal component of the earth’s magnetic field, B0, influences the magnetic field induction, B, due to the bar magnet. At points close to the bar magnet, magnetic induction B due to the bar magnet is very high as compared to the horizontal component of the earth’s magnetic field, B0. Thus, B0is negligible.
According to the inverse square law of magnetism, magnetic field induction B due to the bar magnet decreases as we move away from it. At certain points around the bar magnet, B and B0are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. Therefore, they cancel each other out, and the resultant magnetic field is zero.
Thus, the point where magnetic field induction B due to a bar magnet is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the horizontal component of the earth’s magnetic field induction, B0, is called a neutral point.
The neutral points around a bar magnet can be located in two different cases
- When the north pole of the bar magnet points towards the earth’s north pole
- when the south pole of the bar magnet points towards the earth’s north pole.
When the north pole of a bar magnet points towards the north pole of the earth.
- Fix a sheet of white paper on a drawing board with brass pins.
- Take a compass needle, place it at the centre of the paper, and mark the north and south directions.
- Draw a straight line along the paper connecting the two points. This represents the magnetic meridian of the earth.
- Represent the geographical directions at the corner of the paper.
- Draw an arrow from the geographical south to the geographical north on the right side of the paper to indicate the direction of the horizontal component of the earth’s magnetic field, B0.
- Take a bar magnet and place it at the centre of the paper such that the north pole of the bar magnet points towards the north pole of the earth.
- Now place the compass needle at the north pole of the bar magnet and mark a point where the north pole of the compass needle is.
- Shift the compass such that the south pole of the compass needle is at the point you just marked.
- Mark another point at the north of the compass needle, and then shift the compass, as done earlier.Repeat the procedure till the compass needle reaches the other end of the bar magnet.
- Join all the points to get a continuous smooth curve, which represents a magnetic field line.
- Repeat the procedure from the north pole of the magnet, but from different points, and draw the magnetic field lines.
The two points on either side of the bar magnet at equal distances from its centre, where the compass needle does not show any specific direction. At these points, the magnetic field induction B due to the bar magnet and the horizontal component of the earth’s magnetic field induction, B0are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. The resultant magnetic field is zero. These points represent the neutral points denoted by N1and N2. These two points fall on the equatorial line of the bar magnet.
Thus, when the north pole of a bar magnet points towards the geographical north pole of the earth, the two neutral points lie on the equatorial line of the bar magnet such that they are equidistant from the centre of the bar magnet.
The Angle of Inclination (dip) and Angles of Declination
Measure the angle of inclination (dip) and angles of declination
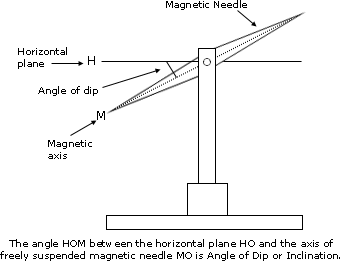
Angle of dip is the angle between the direction of the earth’s magnetic flux and the horizontal.
Measurement of angle of dip
The angle of dip is not constant over the earth’s surface; it varies from place to place.
This difference is brought about by the earth’s magnetic field direction at a point on the earth’s surface. The easiest way to measure the angle of dip is using a thin iron rod.The rod is suspended by length of a thread such that it balances horizontally.
Without disturbing the position of attachment, the rod is magnetised by bringing close a bar magnet and touching. On re-suspending the rod will dip with its north pole pointing downwards as shown in the diagram above. Using a protractor, the angle between the axis of the rod and the horizontal can be measured.
Angle of declination
Is the angle between the magnetic meridian and geographic meridian. The angle of declination varies from place to place all over the world. Maps shows declination at different points of the world.
Application of Earth's Magnetic Field
State the application of earth's magnetic field
The earth’s magnetic field is used to:
- indicate poles of unknown magnets.
- enables the use of magnetic needle.






